JACKSONVILLE, Fla. — We are a little over a month away from the solar eclipse that’s set to take place on April 8! With that in mind, here’s a list of terms you might want to get familiar with:
>>> STREAM ACTION NEWS JAX LIVE <<<
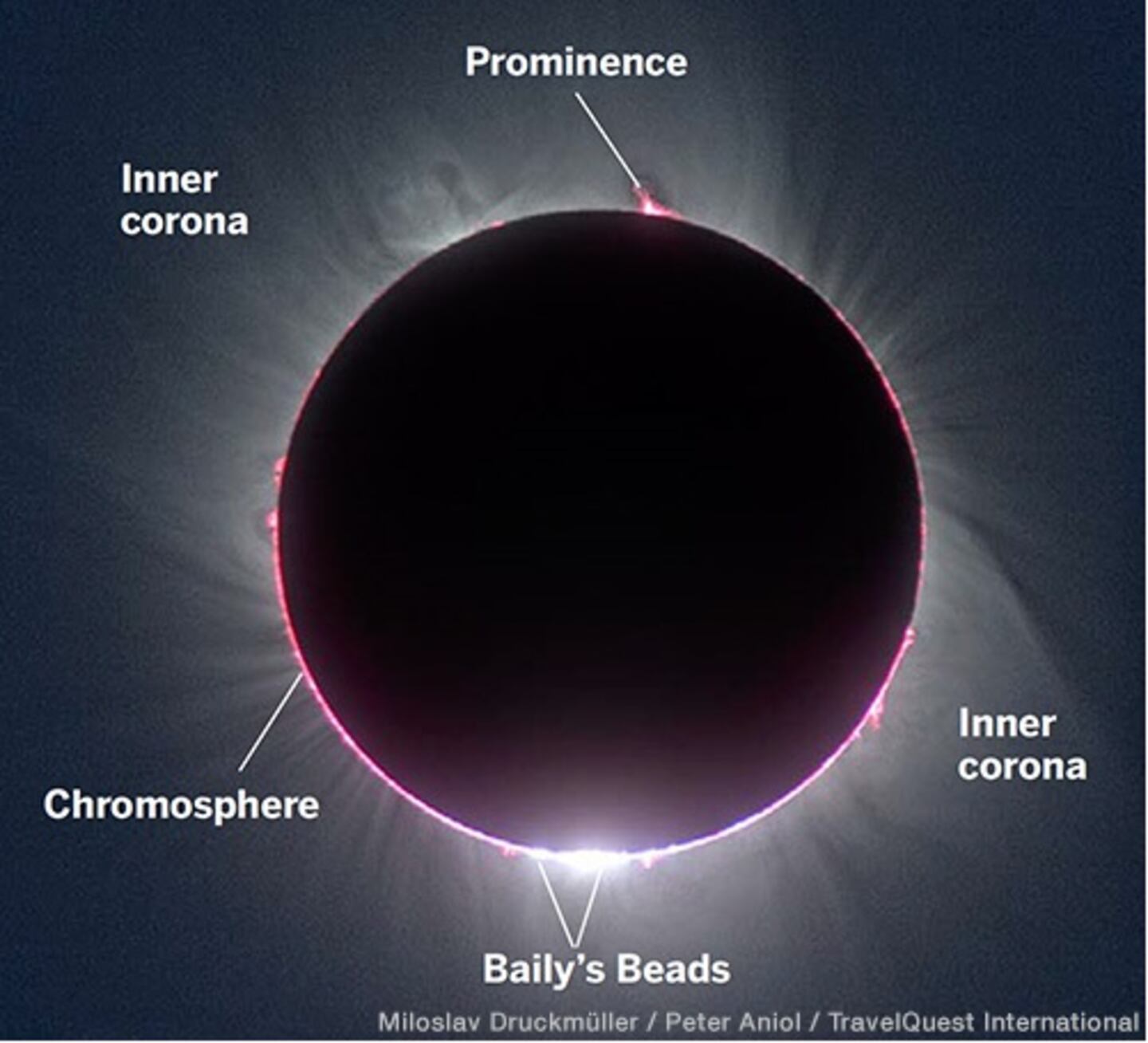
Baily’s Beads: Caused by shafts of sunlight shining through deep valleys on the lunar limb (edge), they look like a series of brilliant beads popping on and off. They appear just before second contact and just after third contact at annular and total solar eclipses. They’re named after the English astronomer Francis Baily, who first described them during the annular eclipse of May 15, 1836.
Chromosphere: A thin, red-colored layer of solar atmosphere located just above the photosphere. It is briefly visible immediately after the second contact and just before the third contact at a total solar eclipse.
Corona: The sun’s upper atmosphere, visible as a pearly glow around the eclipsed sun during totality. Its shape (sometimes elongated, sometimes round) is determined by the sun’s magnetic field and is linked to the sunspot cycle.
Diamond Ring: A single Baily’s Bead, shining like a brilliant diamond set into a pale ring created by the pearly white corona. It’s the signal that totality is about to start (second contact) or has ended (third contact).
Duration: The time between the second and third contact during a total or annular solar eclipse.
Solar eclipse 2024: What time does it start; will I be able to see it; glasses; how to view it?
Eclipse Magnitude: The fraction of the sun’s diameter covered by the moon. It is a ratio of sun/moon diameters and should not be confused with eclipse obscuration (see next term). When the eclipse magnitude is 50% (that is, when 50% of the sun’s diameter is covered), only about 40% of the solar surface area is obscured.
Eclipse Obscuration: The fraction of the sun’s surface area covered by the moon. Do not confuse it with eclipse magnitude (see above). When 50% of the solar surface area is obscured, the eclipse magnitude is roughly 60%.
First Contact (C1): The moment when the moon takes its first tiny nibble out of the solar disk — the beginning of the partial phase of an eclipse.
Looking at over a century of total solar eclipses in the U.S.
Fourth (last) Contact (C4): The instant when the moon no longer covers any part of the solar disk. This signals the conclusion of the partial phase of an eclipse.
New Moon: The lunar phase when the moon is located in the same direction in the sky as the sun. New moon is the only lunar phase during which an eclipse of the sun can occur.
Partial Eclipse: A solar eclipse where the moon covers only a portion of the sun. A partial eclipse precedes and follows totality or annularity, but a partial can also occur by itself. A partial solar eclipse is visible over a wider swath of Earth than is totality or annularity.
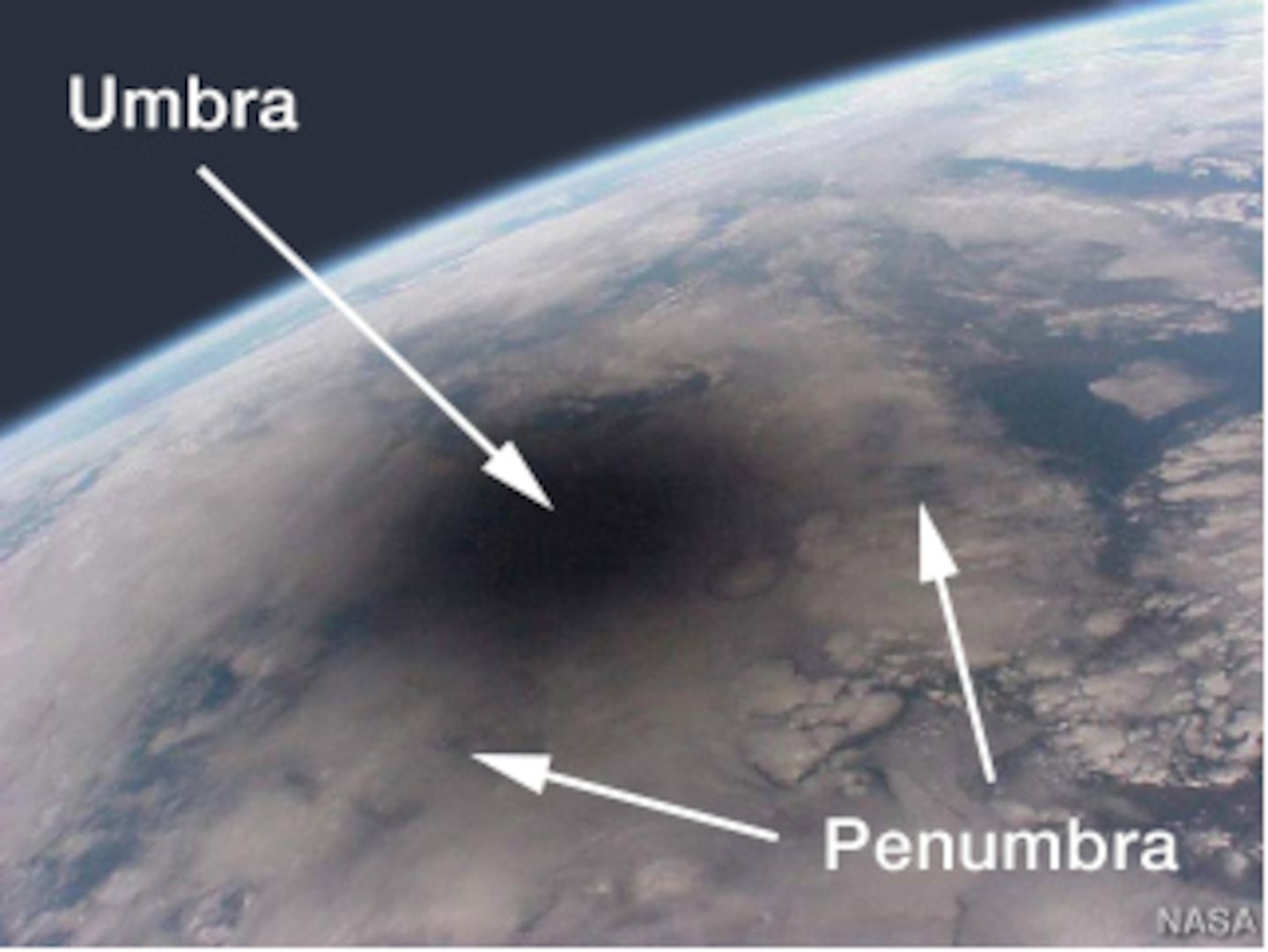
Penumbra: The portion of the moon’s shadow in which only part of the sun is covered. An observer standing in the penumbra sees a partial solar eclipse.
Photosphere: The visible surface of the sun, which consists of a gas layer at a temperature of roughly 5,500° Celsius (10,000° Fahrenheit).
Prominence: Hot gas hanging just above the solar surface, usually appearing as a red-colored arc or filament hovering in the lower part of the corona. Prominences are quickly covered by the moon after the second contact and revealed just before the third contact at a total solar eclipse.
[DOWNLOAD: Free Action News Jax app for alerts as news breaks]
Second Contact (C2): The instant when the total or annular phase of an eclipse begins. For a total eclipse, this is synonymous with the disappearance of the first diamond ring. At second contact during a total solar eclipse, darkness suddenly falls (but only to the level of deep twilight).
Third Contact (C3): The instant when the total or annular phase of a solar eclipse ends. For a total eclipse, this is synonymous with the appearance of the second diamond ring. At third contact during a total solar eclipse, daylight suddenly returns.
Total Eclipse: A solar eclipse where the apparent diameter of the moon is large enough to completely cover the sun’s photosphere (even if only momentarily) and reveal the faint solar corona.
[SIGN UP: Action News Jax Daily Headlines Newsletter]
Totality: The maximum phase of a total solar eclipse, during which the moon’s disk completely covers the sun’s bright face. Totality occurs between the second and third contact. It can last from a fraction of a second to a maximum of 7 minutes 31 seconds.
Umbra: The darkest part of the moon’s shadow, within which the entirety of the sun’s bright face is blocked. Within the umbra, the moon appears larger than the sun. An observer standing in the umbra sees a total solar eclipse.
Umbraphile: A solar-eclipse aficionado; a person who will do almost anything, and travel almost anywhere, to see totality. Also known as “eclipse chaser.”
Credit: American Astronomical Society
Click here to download the free Action News Jax news and weather apps, click here to download the Action News Jax Now app for your smart TV and click here to stream Action News Jax live.